Title: Leveraging AI for Cybersecurity: Building a Malware Detector
In today's digital age, cybersecurity is more critical than ever. With the proliferation of malware and cyber threats, organizations are constantly seeking innovative solutions to protect their systems and data. One promising approach involves leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to build advanced malware detectors capable of identifying and mitigating threats in real-time.
Understanding the Role of AI in Cybersecurity
AI holds immense potential in the field of cybersecurity due to its ability to analyze vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI systems can detect patterns and anomalies indicative of malicious activity, thereby bolstering defense mechanisms against cyber threats.
In the context of malware detection, AI can automate the process of identifying and classifying malicious software, enabling organizations to respond promptly to potential security breaches. Moreover, AI-powered malware detectors can adapt and evolve over time, staying ahead of emerging threats and evolving attack vectors.
Building a Malware Detector Using AI
Let's delve into the process of building a malware detector using AI. While the following steps provide a high-level overview, it's essential to recognize that implementing a robust solution requires careful consideration of various factors, including dataset quality, model architecture, and performance evaluation.
- Data Collection: Gather a diverse dataset comprising both benign and malicious samples of malware. This dataset serves as the foundation for training the AI model to differentiate between normal and malicious behavior.
- Feature Extraction: Identify relevant features from the dataset, such as file properties, system calls, and network activities. These features serve as input variables for training the malware detection model.
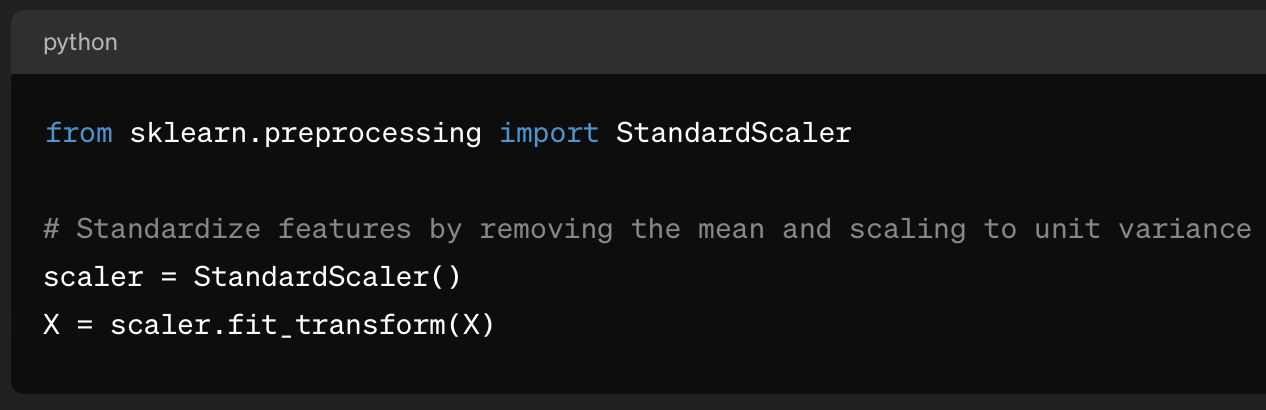
- Preprocessing: Clean and preprocess the data to ensure consistency and remove noise.
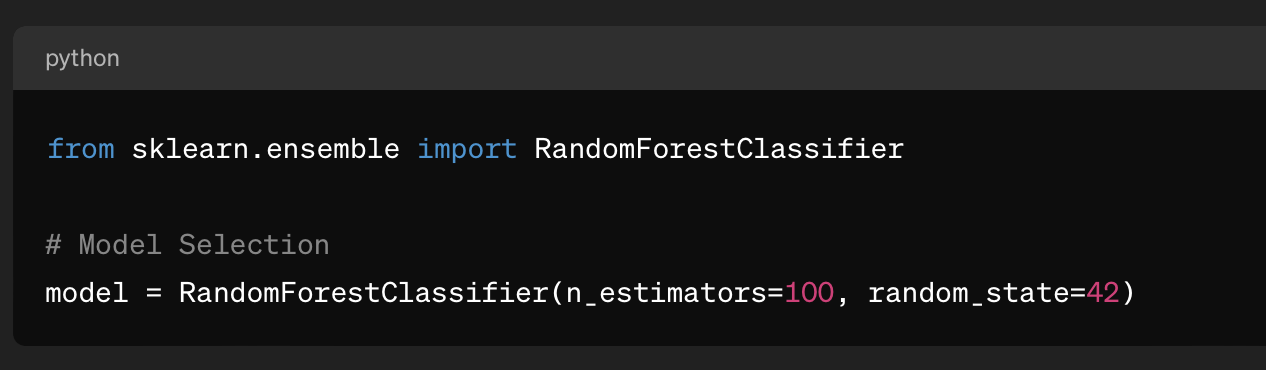
- Model Selection: Choose an appropriate machine learning model for malware detection.
- Training: Train the selected model using the labeled dataset.
- Validation and Testing: Evaluate the trained model's performance using a separate dataset not seen during training.
- Integration: Integrate the trained model into existing cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Monitoring and Updates: Continuously monitor the performance of the deployed model in a production environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI offers immense potential for enhancing cybersecurity, particularly in the realm of malware detection. By leveraging advanced machine learning techniques, organizations can develop robust malware detectors capable of identifying and mitigating security threats in real-time. However, building an effective AI-powered malware detector requires careful consideration of various factors, including data quality, model selection, and performance evaluation. By embracing AI-driven cybersecurity solutions, organizations can bolster their defenses against cyber threats and safeguard their systems and data from malicious actors.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, AI stands as a powerful ally in the ongoing battle against cyber threats, empowering organizations to stay one step ahead in the face of adversity.




Comments
Post a Comment